The living Organisms and Their Surroundings (Worksheet)
Fill in the blanks by choosing the right word from the following set of words.
terrestrial, blowholes, gills, abiotic, ostrich, pines, habitat, stimuli, aquatic, webbed, omnivores, casuarina, locomotion, excretion, chicken
② ___________ egg is the biggest cell in nature.
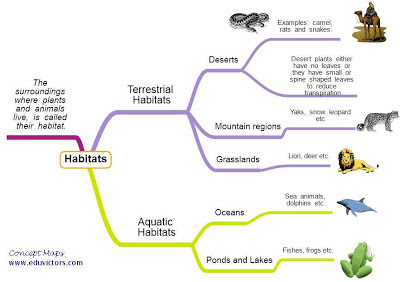
③ There are many types of habitats, however, these may be broadly grouped as __________ (on the land) and ________ (in water).
④ _________ are the respiratory organs of fish.