Economics - CONSUMER RIGHTS (Q & A)
Q1: What factors gave birth to consumer movement in India.
Answer: In India 'social force' led the consumer movement. Rampant food shortages, hoarding, black marketing, adulteration of food and edible oil gave birth to the consumer movement in an organized form in the 1960s.
Following are the main factors that gave rise to consumer movement in India:
⑴ The dissatisfaction of the consumers regarding the market practices
⑵ The gradual withdrawal of the government from production fields after the introduction of New Economic Policy.
⑶ Increasing awareness of the people
⑷ Increasing unfair trade practices
⑸ Emergences of foreign companies
A major step taken by the Indian govt was enactment of Consumer Protection Act 1986 (COPRA).
Q2: What are the rights of the consumers?
Answer:
⑴ Right to be informed
⑵ Right to choose
⑶ Right to safety
⑷ Right to seek redressal
⑸ Right to represent
⑹ Right to consumer education
Q3: Write a short note on the Consumer Protection Act, 1986 (COPRA).
Answer: In 1986, the govt of India enacted the Consumer Protection Act (COPRA) which led to the formation of a three tier quasi judicial machinery at the district, state & national levels for redressal of consumer disputes. The district level court deals with cases involving claims up to Rs 20 lakhs, the state level courts between ₹ 20 lakhs to ₹ 1 crore and the national level court deal with cases involving claims exceeding 1 crore. This Act has enabled the consumers to have the right to represent in the consumer courts.
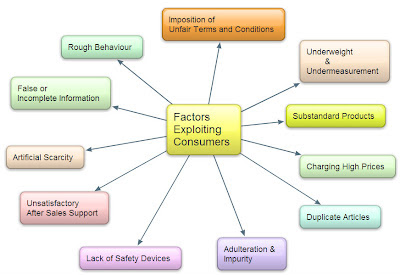
Q4: What are the ways by which consumers get exploited in the market?
Answer: Following are the most common ways by which consumers get exploited in the market:
⑴ Higher price
Traders sometimes charge a price higher than the reteil price (MRP).
⑵ Quality lapse or Substandard quality
Selling of medicines beyond their expiry date, supply of defective home appliances etc. are the activities by traders in which they sell substandard quality of goods.
⑶ Underweight & under measurement
⑷ False information and promises
⑸ Poor after sale service
⑹ Rude behavior
⑺ Inadequate safety measures
⑻ Market malpractices such as adulteration black marketing, duplicate articles etc.
Q5: What are the reasons for exploitation of consumers?
Answer:
⑴ Lack of awareness
⑵ Lack of information about goods & markets
⑶ Limited supplies and competitions.
⑷ Lack of government support to consumers
⑸ Lack of interest on the part of the consumers in responding
⑹ Inadequacy of consumer movement
Q6: How government protects the interests of consumers?
Answer: Government has taken 3 measures to protect the interest of consumers.
⑴ Legislative measures : The government enacted a law called Consumer Protection Act in 1986. The act provides for the establishment of consumer dispute redressal mechanisms at district, state and national levels.
⑵ Administrative measures : Public Distribution System (PDS) started by Government to prevent hoarding and black marketing.
⑶ Technical measures : Setting up institutions for fixing up the standards for products like Indian Standards Institutes, are technical measures taken by Government.
Q7: What are the salient features of COPRA 1986?
Answer: salient features of COPRA 1986 are:
⑴ It applies to all goods and services.
⑵ It covers all the sections whether Private, Public or Cooperative.
⑶ It offers various rights to the consumers.
⑷ It establishes consumer protection councils at the central and state and district levels to promote and protect the right of the consumers.
⑸ It provides separate three- tier quasi-judicial machinery at the national state and district levels. at the national level if is known as National Consumer Court (Commission) at the state level ,it is known as State consumer court (commission)and at the District level, it is called District forum.
⑹ Provisions of the Act are compensatory in nature.
Q8: What are the duties of the Consumer?
Answer: Consumer duties are:
⑴ Be alert about the price and quality of goods and services.
⑵ To assert and act to ensure that he gets a fair deal.
⑶ To organize together to promote the interest of the consumers.
⑷ To purchase quality marked goods such as ISI, AGMARK etc.
⑸ To insist a cash memo after every purchase.
⑹ To make complaints for genuine grievances.

No comments:
Post a Comment
We love to hear your thoughts about this post!
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.