Chapter 1 - Introduction to Accounting
CBSE Class 11 - Accountancy - Q & A
Q1: Define Accounting.
Answer: Accounting can be defined as a process of identifying, recording, classifying, summarizing and communicating economic data.
The introduction of accounting helps the decision-makers of a company to make effective choices, by providing information on the financial status of the business. Today, accounting is used by everyone and a good understanding of it is beneficial to all.
Accountancy acts as a language of finance.
1. To maintain a systematic record of business transactions.
Accounting is used to maintain a systematic record of all the financial transactions in a book of accounts.
For this, all the transactions are recorded in chronological order in Journal and then posted to principle book i.e. Ledger.
2. To ascertain profit and loss
Every businessman is keen to know the net results of business operations periodically.
To check whether the business has earned profits or incurred losses, we prepare a “Profit & Loss Account”.
3. To determine the financial position
Another important objective is to determine the financial position of the business to check the value of assets and liabilities.
For this purpose, we prepare a “Balance Sheet”.
4. To provide information to various users
Providing information to the various interested parties or stakeholders is one of the most important objectives of accounting.
It helps them in making good financial decisions.
5. To assist the management
By analysing financial data and providing interpretations in the form of reports, accounting assists management in handling business operations effectively.
Q3: What do you mean by the accounting cycle?
Answer: The accounting cycle means the sequence of steps in accounting for a financial transaction
entered into by an organisation.
Q4: What are the functions or steps of the accounting process?
Answer: Following attributes or major steps that can be drawn from the definition of Accounting:
① Identifying and Measurement
② Recording
③ Classifying
④ Summarizing
⑤ Analysis, Interpretation and Communication
(1) Identifying financial transactions and events
Accounting records only those transactions and events which are of financial nature. So, first of all, such transactions and events are identified.
The first step in accounting is to determine what to record, i.e., to identify the financial events which are to be recorded in the books of accounts. It involves observing all business activities and selecting those events or transactions which can be considered as financial transactions.
(2) Measuring the transactions
Accounting measures the transactions and events in terms of money which are considered as a common unit.
In Accounting, we record only those transactions which can be measured in terms of money or which are of financial nature. If a transaction or event cannot be measured in monetary terms, it is not considered for recording in financial accounts.
There are few events directly or indirectly make an affect on the working of a business firm but cannot be recorded in the books of accounts because they cannot be measured in terms of money.
For example, the appointment of a new managing director, signing of contracts, strikes, death of an employee etc is not shown in the books of accounts.
(3) Recording of transactions
Accounting involves recording the financial transactions inappropriate book of accounts such as Journal or Subsidiary Books.
A transaction will be recorded in the books of accounts only if it is considered as an economic event and can be measured in terms of money. Once the economic events are identified and measured in financial terms, these are recorded in books of account in monetary terms and in chronological order. The recording should be done in a systematic manner so that the information can be made available when required.
(4) Classifying the transactions
Transactions recorded in the books of original entry - Journal or Subsidiary books are classified and grouped according to nature and posted in separate accounts known as ‘Ledger Accounts’.
Once the financial transactions are recorded in journal or subsidiary books, all the financial transactions are classified by grouping the transactions of one nature at one place in a separate account. This is known as the preparation of Ledger.
(5) Summarising the transactions
It involves presenting the classified data in a manner and in the form of statements, which are understandable by the users.
It includes Trial balance, Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet.
It is concerned with the presentation of data and it begins with a balance of ledger accounts and the preparation of trial balance with the help of such balances. Trial balance is required to prepare the financial statements i.e. Trading Account, Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet.
(6) Analysing and interpreting financial data
Results of the business are analysed and interpreted so that users of financial statements can make a meaningful and sound judgment.
The main purpose of accounting is to communicate the financial information the users who analyse them as per their individual requirements.
(7) Communicating the financial data or reports to the users
Communicating the financial data to the users on time is the final step of Accounting so that they can make appropriate decisions. Providing financial information to its users is a regular process.
Q5: Define transaction.
Answer: A transaction is any financial event which involves an exchange of goods and services between two or more persons.
Q6: Name the types of a business transaction?
Answer:
(a) Cash Transaction,
(b) Credit Transaction.
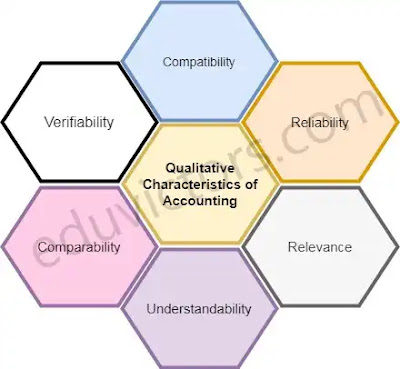
Q7: What are the qualitative characteristics of accounting?
Answer: Qualitative characteristics are the attributes of accounting information, which
enhance its understandability and usefulness:
① Reliability
② Relevance
③ Understandability
④ Comparability
① Reliability
Reliability implies that the information must be free from material error and personal bias.
② Relevance
Accounting information must be relevant to the decision-making requirements of the users.
③ Understandability
Information should be disclosed in financial statements in such a manner that these are easily understandable.
④ Comparability
Both intra-firm and inter-firm comparison must be possible over different time periods.
☞See also:
Chapter 1: Basic Terms
Accountancy Sample Question Paper (2016-17)
Accountancy Mid-Term Sample Question Paper (2019-20)
Accountancy (Syllabus) - 2017-18
Chapter 2 - Systems and Basis of Accounting (Revision Notes)
Chapter 2 - Introduction to Book Keeping (Study Notes)
Chapter 2 - Advantages of Book Keeping
Accounting is a service activity. Its function is to provide quantitative information, primarily financial in nature, about economic entities that is intended to be useful in making economic decisions.
Q2: State the objectives of accounting.
Answer:
Objectives of Accounting are:
1. To maintain a systematic record of business transactions.
Accounting is used to maintain a systematic record of all the financial transactions in a book of accounts.
For this, all the transactions are recorded in chronological order in Journal and then posted to principle book i.e. Ledger.
2. To ascertain profit and loss
Every businessman is keen to know the net results of business operations periodically.
To check whether the business has earned profits or incurred losses, we prepare a “Profit & Loss Account”.
3. To determine the financial position
Another important objective is to determine the financial position of the business to check the value of assets and liabilities.
For this purpose, we prepare a “Balance Sheet”.
4. To provide information to various users
Providing information to the various interested parties or stakeholders is one of the most important objectives of accounting.
It helps them in making good financial decisions.
5. To assist the management
By analysing financial data and providing interpretations in the form of reports, accounting assists management in handling business operations effectively.
Q3: What do you mean by the accounting cycle?
Answer: The accounting cycle means the sequence of steps in accounting for a financial transaction
entered into by an organisation.
Q4: What are the functions or steps of the accounting process?
Answer: Following attributes or major steps that can be drawn from the definition of Accounting:
① Identifying and Measurement
② Recording
③ Classifying
④ Summarizing
⑤ Analysis, Interpretation and Communication
(1) Identifying financial transactions and events
Accounting records only those transactions and events which are of financial nature. So, first of all, such transactions and events are identified.
The first step in accounting is to determine what to record, i.e., to identify the financial events which are to be recorded in the books of accounts. It involves observing all business activities and selecting those events or transactions which can be considered as financial transactions.
(2) Measuring the transactions
Accounting measures the transactions and events in terms of money which are considered as a common unit.
In Accounting, we record only those transactions which can be measured in terms of money or which are of financial nature. If a transaction or event cannot be measured in monetary terms, it is not considered for recording in financial accounts.
There are few events directly or indirectly make an affect on the working of a business firm but cannot be recorded in the books of accounts because they cannot be measured in terms of money.
For example, the appointment of a new managing director, signing of contracts, strikes, death of an employee etc is not shown in the books of accounts.
(3) Recording of transactions
Accounting involves recording the financial transactions inappropriate book of accounts such as Journal or Subsidiary Books.
A transaction will be recorded in the books of accounts only if it is considered as an economic event and can be measured in terms of money. Once the economic events are identified and measured in financial terms, these are recorded in books of account in monetary terms and in chronological order. The recording should be done in a systematic manner so that the information can be made available when required.
(4) Classifying the transactions
Transactions recorded in the books of original entry - Journal or Subsidiary books are classified and grouped according to nature and posted in separate accounts known as ‘Ledger Accounts’.
Once the financial transactions are recorded in journal or subsidiary books, all the financial transactions are classified by grouping the transactions of one nature at one place in a separate account. This is known as the preparation of Ledger.
(5) Summarising the transactions
It involves presenting the classified data in a manner and in the form of statements, which are understandable by the users.
It includes Trial balance, Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet.
It is concerned with the presentation of data and it begins with a balance of ledger accounts and the preparation of trial balance with the help of such balances. Trial balance is required to prepare the financial statements i.e. Trading Account, Profit & Loss Account and Balance Sheet.
(6) Analysing and interpreting financial data
Results of the business are analysed and interpreted so that users of financial statements can make a meaningful and sound judgment.
The main purpose of accounting is to communicate the financial information the users who analyse them as per their individual requirements.
(7) Communicating the financial data or reports to the users
Communicating the financial data to the users on time is the final step of Accounting so that they can make appropriate decisions. Providing financial information to its users is a regular process.
Q5: Define transaction.
Answer: A transaction is any financial event which involves an exchange of goods and services between two or more persons.
Q6: Name the types of a business transaction?
Answer:
(a) Cash Transaction,
(b) Credit Transaction.
Q7: What are the qualitative characteristics of accounting?
Answer: Qualitative characteristics are the attributes of accounting information, which
enhance its understandability and usefulness:
① Reliability
② Relevance
③ Understandability
④ Comparability
① Reliability
Reliability implies that the information must be free from material error and personal bias.
② Relevance
Accounting information must be relevant to the decision-making requirements of the users.
③ Understandability
Information should be disclosed in financial statements in such a manner that these are easily understandable.
④ Comparability
Both intra-firm and inter-firm comparison must be possible over different time periods.
☞See also:
Chapter 1: Basic Terms
Accountancy Sample Question Paper (2016-17)
Accountancy Mid-Term Sample Question Paper (2019-20)
Accountancy (Syllabus) - 2017-18
Chapter 2 - Systems and Basis of Accounting (Revision Notes)
Chapter 2 - Introduction to Book Keeping (Study Notes)
Chapter 2 - Advantages of Book Keeping


No comments:
Post a Comment
We love to hear your thoughts about this post!
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.