Blog provides NCERT solutions, CBSE, NTSE, Olympiad study material, model test papers, important Questions and Answers asked in CBSE examinations. References to Educational Sites and resources.
Wednesday, 21 May 2025
Class 11 Applied Maths | Sets and Relations | Holidays Homework 2025
Monday, 24 March 2025
Class 11 Mathematics | NCERT Exercise 2.3 | Solved Answers and Questions #eduvictors #class11Maths
Class 11 Mathematics | NCERT Exercise 2.3 | Solved Answers and Questions
Q1. Which of the following relations are functions? Give reasons. If it is a function, determine its domain and range.
(i) {(2,1), (5,1), (8,1), (11,1), (14,1), (17,1)}
(ii) {(2,1), (4,2), (6,3), (8,4), (10,5), (12,6), (14,7)}
(iii) {(1,3), (1,5), (2,5)}.

Saturday, 15 March 2025
Class 11 Mathematics | NCERT Exercise 2.2 | Solved Answers and Questions #eduvictors #class11Maths
Class 11 Maths | NCERT Exercise 2.2 | Solved Answers and Questions
Q1. Let A = {1, 2, 3,...,14}. Define a relation R from A to A by R = {(x, y): 3x – y = 0, where x, y ∈ A}. Write down its domain, codomain and range.

Thursday, 6 March 2025
Class 11 Maths | NCERT Exercise 2.1 | Solved Answers and Questions | #eduvictors
Class 11 Maths | NCERT Exercise 2.1 | Solved Answers and Questions
RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
Q1. If (x/3 + 1, y - 2/3) = (5/3, 1/3), find the values of x and y.
Answer: Since ordered pairs are equal,
∴ x/3 + 1 = 5/3
⇒ x/3 = 5/3 - 1 = 2/3
⇒ x = 2
y - 2/3 = 1/3
y = 1/3 + 2/3
y = 3/3 = 1
Thus, x = 2 and y = 1

Thursday, 22 December 2022
National Mathematics Day #eduvictors
National Mathematics Day

Thursday, 28 July 2022
Class 11 - Maths - Trigonometric Functions Notes, Solved Problems and NCERT Exercise 3.2 Solutions #eduvictors #class11Maths #Trigonometry
Class 11 - Maths - Trigonometric Functions Notes, Solved Problems and NCERT Exercise 3.2 Solutions

Wednesday, 27 July 2022
Monday, 27 June 2022
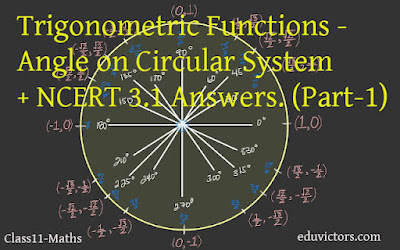
Class 11 - Maths - Trigonometric Functions - Angle on Circular System + NCERT 3.1 Answers. (Part-1) #class11Maths #eduvictors #trigonometry
Class 11 - Maths - Trigonometric Functions - Angle on Circular System + NCERT 3.1 Answers. (Part-1)
You should remember
1. In the sexagesimal system, we measure angles in degrees, minutes and seconds.
1 right angle = 90°
1° = 60′ (minute) and
1′ = 60′′ (second)
2. In the circular measure, we measure angles in radians.
Thus,
πc = 180°
Friday, 25 March 2022
Methods of Differentiation - CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-11 #class11Maths #limits #calculus #differentiation #eduvictors
Methods of Differentiation
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-11
Working rule for finding the derivative of implicit functions
First method:
Differentiate every term of f (x, y) = 0 with respect to x.

Tuesday, 15 February 2022
DIFFERENTIATION OF STANDARD FUNCTIONS- CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-10 #class11Maths #limits #calculus #differentiation #eduvictors
DIFFERENTIATION OF STANDARD FUNCTIONS
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-10
You have learnt theorems of differentiation part-9. Let us proceed further. Here is a list of differentiation of some standard functions:

Sunday, 6 February 2022
THEOREMS ON DIFFERENTIATION - CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-9 #class11Maths #limits #calculus #differentiation #eduvictors
THEOREMS ON DIFFERENTIATION
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-9
You have learnt about finding derivatives using the first principle in part-7 and part-8. Let us proceed further. Here is a summary of theorems on differentiation.

Sunday, 30 January 2022
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-8 Differential CoEfficient and Derivatives Using First Principle #class11Maths #limits #calculus #differentiation #eduvictors
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-8
 |
| Differentiation |

Wednesday, 12 January 2022
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives (Part-7) Derivatives Using First Principle #class11Maths #limits #calculus #differentiation #eduvictors
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-7
Derivatives Using First Principle

Friday, 31 December 2021
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives (Part-6) - Derivative of a Function At a Point #limits #class11Maths #calculus #eduvictors
Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives (Part-6) - Derivative of a Function At a Point
Q1: What is the derivative of a function at a point?
Answer: Let y = f(x) is a continuous function. It means the value of y changes as the value of x changes.
At x = a, is a point in its domain of definittion. The derivative of f at a is defines as:

Saturday, 25 December 2021
Class 11 and 12 Maths - Probability - Part 1 (Solved Questions) #probability #class11Maths #class12Maths #cbse202122 #eduvictors
Class 11 & 12 Maths - Probability - Part 1 (Solved Questions)
Let us revisit the basic terminology used in probability.
Q1: Define probability. What can the probability never predict?
Answer: Probability gives us a measure of the likelihood that something will happen. However, probability can never predict the number of times that an occurrence actually happens.
Q2: Define experiment.
Answer: An action or operation resulting in two or more well-defined outcomes.
e.g. tossing a coin, throwing a die, drawing a card from a pack of well-shuffled playing cards etc.

Wednesday, 22 December 2021
National Mathematics Day #mathematics #eduvictors
National Mathematics Day
*Typo in the graphic new = knew
Sunday, 19 December 2021
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-5 #class11Maths #eduvictors #limits #calculus
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-5

Wednesday, 1 December 2021
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-4- Limits of Trigonometric Functions #class11Maths #eduvictors #limits
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives Part-4- Limits of Trigonometric Functions

Sunday, 14 November 2021
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives (Part-3) Questions and Answers #class11Maths #Limits #eduvictors
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives
Part-3 Algebra of Limits
In the previous post Limits and derivatives Part-2, we get basic ideas of the algebra of limits and also learned about rules and properties of limits.
Let us try to solve few problems:
Q1: Evaluate the given limit $\lim_{r\rightarrow 1} \pi r^2$
Answer: $\lim_{r\rightarrow 1} \pi r^2 = \pi(1)^2 = \pi$

Wednesday, 10 November 2021
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives (Part-2) Questions and Answers #class11Maths #Limits #eduvictors
CBSE Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives (Part-2)
Questions and Answers #class11Maths #Limits
In the previous blog post Limits and derivatives Part-1 , we learn
$\lim_{x\rightarrow a} f(x) = l$ and it is called limit of the function f(x)
① The two ways x could approach a number an either from left or from right, i.e., all the values of x near a could be less than a or could be greater than a.
② In this case the right and left hand limits are different, and hence we say that the limit of f(x) as x tends to zero does not exist (even though the function is defined at 0).


