Class 11 - Mathematics - Limits and Derivatives (Part-6) - Derivative of a Function At a Point
Q1: What is the derivative of a function at a point?
Answer: Let y = f(x) is a continuous function. It means the value of y changes as the value of x changes.
At x = a, is a point in its domain of definittion. The derivative of f at a is defines as:
$\lim_{x\rightarrow a} \frac{f(x) - f(a)}{x -a}$
provided limit exists.
Equivalently, it can be defined as $\lim_{h\rightarrow 0} \frac{f(a + h) - f(a)}{h}$
provided this limit exists. Derivative of f(x) at a is denoted by f'(a) or $\frac{dy}{dx}$.
Q2: What is the use of finding a derivative of a function at a point?
Answer: It helps in estimating the rate of change, or the rate at which one variable changes in relation to another variable.
e.g. find the instantaneous velocity i.e. value of the velocity at that particular instant of time. Or finding an estimate of how a stock price will change at its present value.
Q3: What is differentiation?
Answer: The process of finding the derivative is known as differentiation. This method is also called differentiation from the first principle or ab-initio method or delta method.
Q4: Find the derivative of $x^2 - 2$ at x = 10.
Answer: Derivative of f(x) at x = a is given by
f'(a) = $\lim_{h\rightarrow 0} \frac{f(a + h) - f(a)}{h}$
Here f(x) = $x^2 - 2$
Given, a = 10,
∴ f(10 + h) = $(10+h)^2 - 2$ and f(10) = $(10)^2 - 2$
Thus,
f(10 + h) - f(10) = $[(10+h)^2 - 2] - (10)^2 - 2$
= $(10+h)^2 - 10^2$
= (20 + h)h
∴ f'(10) = $ \lim_{h\rightarrow 0} \frac{f(10 + h) - f(10)}{h}$
= $\lim_{h\rightarrow 0} \frac{h(20+h)}{h}$
= $\lim_{h\rightarrow 0} (20+h)$
= 20
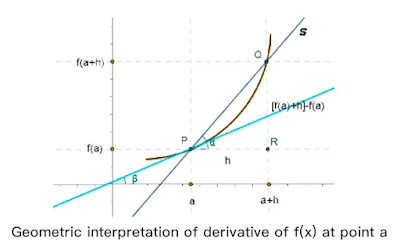
Q5: Show the geometric interpretation of the derivative of a function at a point.
Answer: The figure below shows two points and P and Q close to each other.
P and Q are the points of a function y = f(x).
∴ P = (a, f(a)) and Q=(a+h,f(a+h)
Slope of the chord PQ = $\frac{f(a+h) -f(a)}{a + h -a}$
= $\frac{f(a+h) -f(a)}{h}$
As Q comes closer to P, the chord QP approaches the tangent at P.
Thus $h\rightarrow 0$.
∴ $\lim_{h\rightarrow 0} \frac{f(a+h) -f(a)}{h} = \lim_{Q\rightarrow P}tan \beta $
⇒ f′(a) = the slope of the tangent at P.
Q6: Find the derivative of 99x at x = 100.
Answer: Derivative of f(x) at x = 100 is:
f'(100) = $\lim_{h\rightarrow 0} \frac{f(100+h) -f(100)}{h} $
Given, f(x) = 99x
f(100+h) = 99(100+h) and f(100) = 99(100)
∴ f(100+h) - f(100) = 99(100+h) - 99(100)
= 99(100+h - 100)
= 99h
∴ f'(100) = $\lim_{h\rightarrow 0} \frac{99h}{h}$
f'(100) = 99
In the next post, we'll study some important Derivatives Using the First Principle.
👉See Also:
Ch5: Complex Numbers (Part 1) - Solved Problems
Ch 13 Limits and Derivatives (Q & A ) Part -1
Ch 13 Limits and Derivatives (Q & A) Part - 2
Ch 13 Limits and Derivatives (Q & A) Part - 3
Ch 13 Limits and Derivatives (Q & A) Part- 4

No comments:
Post a Comment
We love to hear your thoughts about this post!
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.