Class 11 - Maths - Trigonometric Functions Notes, Solved Problems and NCERT Exercise 3.2 Solutions
Q1. What are quadrantal angles?
Answer: All angles which are integral multiples of π/2 are called quadrantal angles.
Therefore, for quadrantal angles, we have
cos 0° = 1,
sin 0° = 0,
cos $\frac{π}{2}$ = 0
sin $\frac{π}{2}$ = 1
cos π = − 1
sin π = 0
cos $\frac{3π}{2}$ = 0
sin $\frac{3π}{2}$ = -1
cos 2π = 1
sin 2π = 0
Trigonometric Functions
sin x = 0 implies x = nπ, where n is any integer
cos x = 0 implies x = (2n + 1) $\frac{π}{2}$, where n is any integer
Other Trigonometric Functions are:
cosec x = $\frac{1}{sin x}$, x ≠ nπ, where n is an integer
sec x = $\frac{1}{cos x}$, x ≠ (2n + 1)$\frac{π}{2}$, where n is any integer
tan x = $\frac{sin x}{cos x}$, x ≠ (2n + 1)$\frac{π}{2}$, where n is any integer
cot x = $\frac{cos x}{sin x}$, ≠ nπ, where n is any integer
Trignometry Identies:
sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
sec²θ - tan²θ = 1
cosec²θ - cot²θ = 1
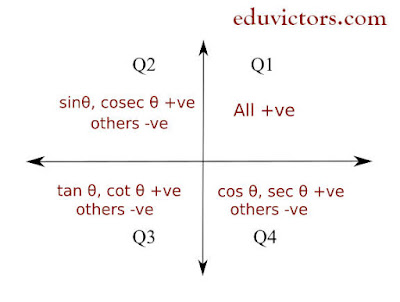
Trigonometric ratios of various angles:
(sin θ)(cosec θ) = 1, θ ≠ nπ, where n ∈ Z
(cos θ)(sec θ) = 1, θ ≠
Q2. Find the values of the other five trigonometric functions if , cos x = $\frac{-1}{2}$ lies in the third quadrant.
Answer: cos x = $\frac{-1}{2}$
∴ sec x = $\frac{1}{cos x} = \frac{1}{\frac{-1}{2}} $
∴ sec x = -2
Since, sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
∴ sin²x = 1 - cos²x
sin²x = 1 - $(\frac{-1}{2})^{2}$
sin²x = 1 - $\frac{1}{4}$
sin²x = $\frac{3}{4}$
sin x = ±$\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
Since x lies in the 3rd quadrant, the value of sin x will be negative
∴ sin x = -$\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
cosec x = $\frac{1}{sin x}$
cosex x = $\frac{1}{-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}$
cosec x = $\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$
tan x = $\frac{sin x }{cos x}$
tan x = $\frac{\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}{\frac{-1}{2}}$
tan x = $\sqrt{3}$
cot x = $\frac{1}{tan x}$
cot x = $\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$
Q3. Find the values of the other five trigonometric functions if sin x = $\frac{3}{5}$, x lies in the second quadrant.
Answer: sin x = $\frac{3}{5}$
cosec x = $\frac{1}{sin x} =\frac{1}{\frac{3}{5}}$
cosec x = $\frac{5}{3}$
Since, sin²x + cos²x = 1
cos²x = 1 - sin²x
cos²x = 1 - $(\frac{3}{5})^2$
cos²x = 1 - $\frac{9}{25} = \frac{16}{25}$
cos x = ±$\frac{\sqrt{4}}{5}$
Since x lies in the 2nd quadrant, the value of cos x will be negative.
∴ cos x = -$\frac{\sqrt{4}}{5}$
sec x = $\frac{1}{cos x} = \frac{-5}{4}$
tan x = $\frac{sin x}{cos x} = \frac{-3}{4}$
cot x = $\frac{1}{tan x} = \frac{-4}{5}$
Q4. If $sin \theta = \frac{a- 4}{2}$ then a lies in ?
Answer: Since -1 ≤ sin θ ≤ 1
Thus we have,
-1 ≤ $\frac{a-4}{2}$ ≤ 1
⇒ -2 ≤ a - 4 ≤ 2
⇒ 2 ≤ a ≤ 6
⇒ a ∈ [2, 6]
Important points you should know:
(a) If A + B = 90° or 270°, then
(i) sin²A + sin²B = 1
(ii) cos²A + cos²B = 1
(iii) tan A . tan B = 1
(iv) cot A . cot B = 1
(b) If A + B = 180°, then
(i) cos A + cos B = 0
(ii) sin A - sin B = 0
(iii) tan A + tan B = 0
(c) If A + B = 360°, then
(i) sin A + sin B = 0
(ii) cos A - cos B = 0
(iii) tan A + tan B = 0
Q5. sin²35 + sin²55 =?
Answer: Since 35° + 55° = 90°
∴ sin²35 + sin²55 = 1
Q6. Find the value of the trigonometric function sin 765°
Answer: We know that the values of sin x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°.
∴ sin 765° = sin(2 × 360° + 45°) = sin 45° = $\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
Q7. Find the value of the trigonometric function cosec(–1410°)
Answer: cosec(–1410°) = –cosec(1410°)
We know that the values of cosec x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°.
∴ -cosec(-1410°) = -cosec (4 × 360° - 30°)
= cosec(30°)
= 2
Q8. Find the value of the trigonometric function $\tan{\frac{19\pi}{3}}$
Answer: We know that the values of tan x repeat after an interval of π or 180°
Given $\tan{\frac{19\pi}{3}} = \tan{6\pi + \frac{\pi}{3}}$
= $\tan{\frac{\pi}{3}}$
= tan 60°
= $\sqrt{3}$
👉See Also:
Ch2: Relations and Functions (1 Mark Q & A) Part-1
Ch2: Cartesian Product of Two Sets (Important Points)
Ch2: Relations - Domain, Range and Co-Domain (Solved Problems)
Ch3: Trigonometric Functions + NCERT Ex 3.1
Ch5: Complex Numbers (Part 1) - Solved Problems
Ch 13 Limits and Derivatives (Q & A ) Part -1
Ch2: Cartesian Product of Two Sets (Important Points)
Ch2: Relations - Domain, Range and Co-Domain (Solved Problems)
Ch3: Trigonometric Functions + NCERT Ex 3.1
Ch5: Complex Numbers (Part 1) - Solved Problems
Ch 13 Limits and Derivatives (Q & A ) Part -1


No comments:
Post a Comment
We love to hear your thoughts about this post!
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.