Blog provides NCERT solutions, CBSE, NTSE, Olympiad study material, model test papers, important Questions and Answers asked in CBSE examinations. References to Educational Sites and resources.
Showing posts with label class10-sstudies. Show all posts
Showing posts with label class10-sstudies. Show all posts
Wednesday 7 November 2018
Monday 5 November 2018
CLASS 10 : SOCIAL SCIENCE - CHAPTER : THE AGE OF INDUSTRIALISATION (Q and A) (#cbsenotes)(#eduvictors)
THE AGE OF INDUSTRIALISATION
(Questions and Answers)
Q1: Explain what is meant by proto-industrialisation?Answer:
1. Proto-industrialisation refers to that phase of industrialization which existed in Britain before the growth of factories using mechanical power.
2. Industries during this phase were run with the help of human labour.
3. The proto-industrialisation system was controlled by the merchants.
4. Goods were produced by a vast number of producers working within their family farms and not in the factories.
Q2: In the proto-industrialisation period, why was it difficult for new merchants to set up business in towns?
OR
Why did the merchants move to the countryside to set up their business?
Answer: It was difficult for merchants to set up their business in towns because:
1. Urban crafts and trade guild associations were powerful in the towns. They restricted the entry of new people into the trade.
2. Rulers granted different guilds the monopoly rights to produce and trade in specific products.
So the new merchants turned to the countryside.

Thursday 20 September 2018
Saturday 11 August 2018
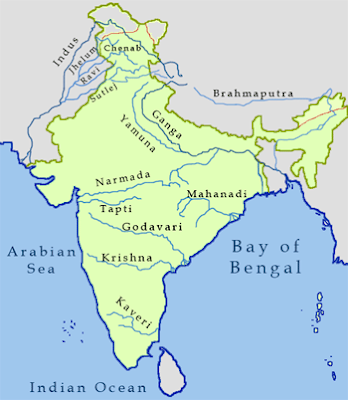
Indian States Touching International Borders - Geography - CBSE Class 6/7/8/9/10/NTSE/CTET -
Indian States Touching International Borders
Table
| No. | Countries | States |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pakistan | 1. Gujarat 2. Rajasthan 3. Punjab 4. Jammu & Kashmir |
Thursday 5 July 2018
CBSE Class 10 - Political Science - Chapter 1. Power Sharing - Revision Assignment (#cbsenotes)(#eduvictors)
Chapter 1. Power Sharing
Revision Assignment
1. What does the word ‘ethnic’ signify?
2. Which language is spoken by the majority of the population in Brussels?
3. What does the term majoritarianism signify?
4. Name the third level government of Belgium.
5. Which city was chosen as the headquarters of the European Union?
6. What does the horizontal power signify?

Monday 2 July 2018
CBSE Class 10 - Economics - Chapter 1 - Development (Revision Assignment) (#cbsenotes)(#eduvictors)
Economics - Chapter 1 -
Development (Revision Assignment)
Q1: What type of aspirations can development fulfill?
Q2: How idea of national development varies?
Q3: Which position was occupied by India in terms of HDI in Human Development Report 2014?
Q4: Which Index is used to compare nutritional level?
Q5: Give one major reason for which children particularly girls are not able to achieve secondary level schooling.

Wednesday 20 June 2018
CBSE Class 10 - Nationalism In India (Very Short Q and A)(#cbsenotes)(#eduvictors)
Nationalism In India
(Very Short Q and A)
Answer: Mental strength is more powerful than physical force to win the heart of the oppressor. The power of truth and the need to search for truth was the philosophy of satyagraha.
This novel idea of Satyagraha was first time implemented by Gandhiji in South Africa.
Q2: Name two Satyagraha movements led by Mahatma Gandhi.
Answer:
① Champaran movement in 1916– to inspire plantation workers to struggle against
② In 1917 Satyagraha at Kheda -to support peasants
Q3: Who is the author of 'Hind Swaraj'?
Answer: Mahatma Gandhi.
Q4: When and where did Jallianwalla Bagh Massacre happen?
Answer: On 13th April 1919 in Amritsar in Punjab.

Wednesday 6 June 2018
CBSE Class 10 - Social Science - Online Quizzes Available (#cbsenotes)(#eduvictors)
Class 10 - Social Science Online Quizzes
Online Quizzes (MCQs) are available for the following chapters:
1. The Rise of Nationalism in Europe.
2. The Age of Industrialisation
3. Popular Struggles and Movements
4. Our Environment - Quiz-1, Quiz-2

Wednesday 23 May 2018
CBSE Class 10 - Geography - Resource and Development (Q and A) (#cbsenotes)(#eduvictors)
Resources and development (Q & A)
Q1: What is Land Degradation? State the human activities which are responsible for land degradation in India?
Answer: When the land becomes unfit for cultivation, it is called land degradation. Activities responsible for land degradation in India are:
⒈ Activities mining
⒉ Overgrazing
⒊ Over irrigation
⒋ Mineral processing
⒌ Industrial effluents
⒈ Activities mining
Surface mining leads to degradation of land. Mining sites are often abandoned after excavation work is complete, leaving deep scars and traces of overburdening. For example deforestation in states like Chhattisgarh Madhya Pradesh and Odisha is due to mining.

Tuesday 10 April 2018
NTSE/ Entrance Exams - Geography - Astronomical Terms (#eduvictors)(#ntsenotes)(#ctetnotes)
ASTRONOMICAL TERMS
THE CELESTIAL SPHERE is an imaginary sphere upon the surface of which all the stars in the sky appear to be studded to an observer stationed at its centre.
THE ZENITH is the intersection of a vertical line through the observer's station with the upper portion of the celestial
sphere. It is the point on the celestial sphere immediately above the observer's station.
THE NADIR is the intersection oI a vertical line through the observer's station with the lower portion oi the celestial sphere. It is the point on the celestial sphere vertically below the observer's stations.

Friday 6 April 2018
CBSE Class 10 - History - The Making of A Global World (Short Questions and Answers) (#cbsenotes)(#eduvictors)
HISTORY - THE MAKING OF A GLOBAL WORLD (Short Q A)
Q1: What was the importance of the Indian trade for the British?
Answer: Indian trade was important for the British for the following reasons:
• Trade Surplus –
Britain had a Trade Surplus with Indian. Britain used this Surplus to balance its trade deficit with other countries.
• Home Charges –
Britain’s trade Surplus in India also helped to pay the so-called home charges that included private remittance by British officials and traders, interest payments on India’s external debt and pensions of British officials in India.
• Major Supplier of cotton –
India remained a major supplier of raw cotton to British which was required to feed the cotton textile industry in Britain.
• Supplier if indentured workers –
Many indentured workers from Bihar, U.P., central India migrated to other countries to work in mines and plantations.
Q2: How did Bretton Woods System Work?

Monday 2 April 2018
CBSE CLASS 10 - HISTORY - THE MAKING OF A GLOBAL WORLD (Very Short Q A) (#cbsenotes)(#eduvictors)
HISTORY - THE MAKING OF A GLOBAL WORLD (Very Short Q A)
Q1: What was the Bretton wood system?
Answer: It was post-war international economic system
Q2: What did indentured labour mean?
Answer: It means bonded Labour
Q3: What were Canal Colonies?
Answer: It stood for irrigated areas.
Q4: Which food travelled west from China to be called ―Spaghetti's?
Answer: Noodles

Wednesday 20 December 2017
Tuesday 12 December 2017
CBSE class 10/9/8/7 - Social Science - Civics- Types of Government (#eduvictors)(#cbseNotes)
Know Different Types of Governments
Republic:
A government whose authority is based on citizen’s votes ,which are represented by elected or nominated officials chosen in free election.
Democracy:
Democracy means ‘rule of people’. The term today refers to political system in which the people or their elected representatives govern themselves.
Communism:
As a system of government, commission is a system of government in which the states owns and operates industry on behalves of the people.

Wednesday 8 November 2017
CBSE Class 10 - Economics - Money and Credit - Concept Points (#eduvictors)(#cbseNotes)
Economics - Money and Credit
Concept Points
✱ People exchange goods and services through the medium of money. Money by itself has no utility. It is only an intermediary. The use of money facilitates exchange.
✱ Direct exchange of goods against goods without use of money is called barter exchange (i.e. exchange of goods for goods). This is also known as CC economy (i.e. commodity for commodity economy).

Thursday 2 November 2017
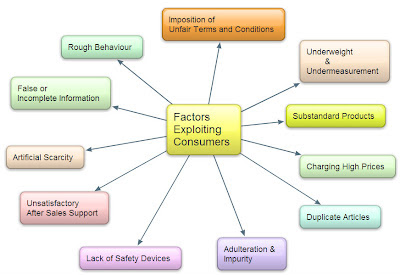
Class 10 - Economics - CONSUMER RIGHTS (Long Q and A) (#cbseNotes)
Economics - CONSUMER RIGHTS (Q & A)
Q1: What factors gave birth to consumer movement in India.
Answer: In India 'social force' led the consumer movement. Rampant food shortages, hoarding, black marketing, adulteration of food and edible oil gave birth to the consumer movement in an organized form in the 1960s.
Following are the main factors that gave rise to consumer movement in India:
⑴ The dissatisfaction of the consumers regarding the market practices
⑵ The gradual withdrawal of the government from production fields after the introduction of New Economic Policy.
⑶ Increasing awareness of the people
⑷ Increasing unfair trade practices
⑸ Emergences of foreign companies
A major step taken by the Indian govt was enactment of Consumer Protection Act 1986 (COPRA).
Q2: What are the rights of the consumers?
Wednesday 11 October 2017
CBSE Class 10 - Economics - GLOBALISATION AND THE INDIAN ECONOMY (Important Points To Remember) (#cbseNotes)
GLOBALISATION AND THE INDIAN ECONOMY
(Important Points To Remember)
 |
| Special Economic Zone |
② An MNC is a company that owns and controls production in more than one nation.
③ Foreign Investment is an investment made by MNCs.
④ Liberalisation means the removal of barriers and restrictions set by the government on foreign trade.

Monday 9 October 2017
CBSE Class 10 - Geography - Minerals and Energy Resources (Short Q and A) (#cbseNotes)
Class 10 - Geography Minerals and Energy Resources (Short Q and A)
Answer: Minerals that occur as alluvial fans in sands of valley floors, and the base of hills.
Q2: Define Rat-hole Mining.
Answer: In the tribal areas of North-East India mining is carried out by individuals or communities illegally. The mining is done in the form of a long narrow tunnel known as Rat hole mining.
Q3: Write two uses of Mica and also areas famous for mica deposits.
Answer: Mica is used in electric and electronic industries
Areas found in:
(a) Gaya-Hazaribagh inJharkhand, and
(b)Ajmer and Beawarin Rajasthan

Monday 25 September 2017
Friday 22 September 2017
CBSE Class 10 - History - Chapter 4 - The Making of a Global World (Important Terms To Remember) (#cbseNotes)
Chapter 4 - The Making of a Global World (Important Terms To Remember)
Trade:
It is an activity of buying selling or exchanging goods or services between people firms or countries.
Silk Route:
The Silk Route is a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East , South , and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa. The name ‘silk routes’ points to the importance of West-bound Chinese silk cargoes along this route.
Indentured Labour:
A bonded labour under contract to work for an employer for a specific amount of time, to pay off his passage to a new country or home.

Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)



