Epidermal Tissue System in Plants
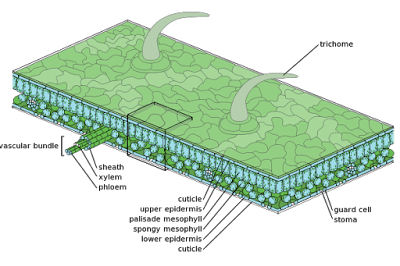 |
| Leaf Structure and Epidermis (image credits: wikimedia) |
1. The outer covering of the plant body is formed of epidermal tissue system.
2. The epidermal tissue system is composed of
ⅰ epidermal cells,
ⅱ stomata and
ⅲ edidermal appendages (trichomes and hairs).
3. Epidermis: The outermost layer of the primary plant body is called epidermis.
4. The epidermis is made up of elongated, compactly arranged cells. These cells form a continuous layer. There is usually a single layer of cells in the epidermis.
5. The epidermal cells are parenchymatous. In these cells, a small amount of cytoplasm lines the cell wall and a large vacuole is present.





