Class 12 - Physics - ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND OPTICS -
About Electromagnetic Spectrum
 |
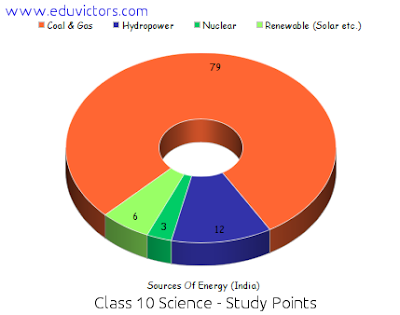
| Electromagnetic Spectrum credits: wikimedia, author: penbaug |
| Name | Wavelength range | Production | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma Rays | 10⁻ⁱ²m | Gamma rays produced in the radioactive decay of the nucleus | In the treatment of cancer and to carry out nuclear reactions. |
| X-Rays | 10⁻⁹m - 10⁻ⁱ²m | x-rays tubes or inner shell electrons | Used as a diagnostic tool in medical to find out fractures in bones. to find cracks, flaws in the metal part of a machine |
| UV Rays | 4×10⁻⁷m - 10⁻⁹m | By very hot bodies like the sun and by UV lamps. | In water purifier in the detection of forged documents, in food preservation. |