Chapter 7 - Conservation of Plants and Animals (Questions and Answers)
CBSE Class 8 - Science
Q1: Define ecology.
Answer: It is the science which deals with the relation between organism and its surrounding environment.
Q2: What is a biome?
Answer: A biome is a large area with similar flora, fauna, and microorganisms. Each biome can have many ecosystems in it. For examples the
tropical rainforests, tundra in the arctic regions, and the evergreen trees in the coniferous forests, each of these contain species that are adapted to the varying conditions of water, heat, and soil in the biome.
For example, polar bears thrive in the arctic by having thick skin while cactus plants preserve water in the hot desert with help of spiny leaves with waxy layer coating.
Q3: Give one use of wood?
Answer: As a fuel, building material.
Q4: Define wild-life.
Answer: All non-domesticated and non-cultivated biota found in the natural habitat is termed as wildlife.
Q5: What is deforestation? What are its causes?
Answer: Deforestation means clearing or cutting of the forest and using these trees or plants for other purposes such as:
- building houses and factories,
- land for cultivation,
- manufacturing furniture and
- using wood as fuel.
In many parts of our country, natural vegetations are destroyed illegally.
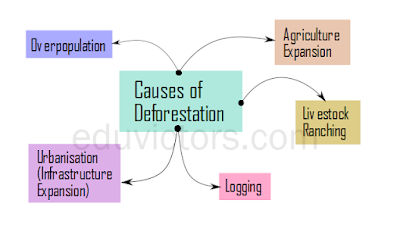
Causes of Deforestation are:
1. Due to the growing population of human beings, there is a worldwide demand for wood for firewood or in construction, paper and furniture as well as clearing land for commercial and industrial development. Such demands have increased with growing local populations.
2. There is a strong demand for agricultural expansion and wood fuel. It has endangered the larger forest areas.
3. There is a growing demand for land required for breeding and rearing of livestock.
4. Logging i,e. cutting and skidding of trees has resulted in large scale deforestation and loss of habitat.
The destruction of significant areas of forest cover has resulted in a degraded environment with reduced biodiversity, In many countries, massive deforestation is going on and is affecting the climate and geography.
Q6: What are the ill-effects of deforestation?
Answer: A few ill-effects of deforestation are:
① Reduced rainfall,
② change in climate,
③ soil erosion,
④ imbalance of greenhouse and global warming
Deforestation is a substantial contributor to global warming, the mass destroying of the worlds rain forests is harmful to the environment.
The incineration, cutting and burning of forest plants in order to clear land releases tonnes of CO₂, which increases the impact of global warming.
The presence or absence of trees can change the quantity of water on the surface, in the soil or groundwater, or in the atmosphere, Deforestation affects the erosion rates and the availability of water for either ecosystem functions or human services.
Q7: How does deforestation lead to global warming?
Answer: Cutting down forest increases the amount of carbon - dioxide in the atmosphere, which can affect climate and destroy the homes of many animals and plants. So deforestation leads to soil erosion, irregular rainfall and global warming.
Q8: Name two agents which contribute 70% of the oxygen in photosynthesis.
Answer: Marin green algae and cyanobacteria.
Q9: Define biosphere.
Answer: The region of the surface and atmosphere of the Earth (or other planets) where living organisms exist is called the biosphere. It is the life-supporting zone of the earth, where atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere meet, interact and make life possible is known as the biosphere.
Q10: What do you mean by biodiversity?
Answer: The variety of (diversity) plant and animal life in a particular habitat -(or in the world as a whole) is called biodiversity. It is the blanket term for natural biological wealth that under guards human life and well being.
Q11: What is flora?
Answer: The natural vegetation (plants) in a particular area is termed as flora.
Q12: What is fauna?
Answer: All the micro-organisms to macro-organisms (animals, birds, etc.) are termed as fauna.
Q13: Define conservation.
Answer: Conservation can be defined as the management of resources in such a manner that the benefits apply to the largest number of people for the longest possible time without harming the natural or ecological balance. Its basic purpose is the restoration of wildlife, flora and fauna to a natural state and maintains equilibrium.
Q14: State the four main objectives of conservation of forests and wildlife.
Answer: Objectives are:
① To promote the ecological security of society.
② To provide for sustainable management of the country's precious biodiversity.
③ To strive for the protection of the environment.
④ To assist forest-dependent communities to co-exist.
Q15: How many species of flora and fauna are found in India?
Answer: So far 45,000 species of plants have been discovered in India. India has a great variety of fauna numbering 81,251 species, which represent 6.67 % of the world’s fauna.
Q16: Name the five types of forests found in India.
Answer:
1. Desert (Dry forests)
2. Deciduous forest
3. Tropical Evergreen forests
4. Hill (mountain) forests
5. Tidal forest
Q17: Name three types of protected areas that are made to conserve forests and wildlife.
Answer: Sanctuary, national park, a biosphere reserve.
Q18: What is the need for conservation of wildlife and forests?
Answer:
1. Wildlife is an asset to be protected and preserved because of their aesthetic, ecological, educational, historical and scientific values.
2. Wildlife is essential for ecological balance.
3. Wildlife is a big boost to tourism and ecological study.
4. The innumerable plants have immense medicinal value.
5. The wildlife is an important source of genetic material useful in genetic engineering.
Q19: What are national parks? State its objectives and features.
Answer: National Park is an area dedicated to protecting the environment, the natural objects and the wildlife therein.
Objective:
- Conservation of species of habitat with minimal or very low intensity of human activity.
Features
- No human resides in the Park, other than a public servant on duty and permitted persons by the Chief Wildlife Warden.
- No outside species are allowed.
- No cutting and No Grazing are allowed
Zone
- Core Zone only
There are 104 existing national parks in India covering an area of 40501.13 km2, which is 1.23% of the geographical area of the country (Source: National Wildlife Database, May 2019). Jim Corbett National Park, Uttarakhand is the first National park of India. It was established in 1936.
Q20: What are Sanctuaries or wildlife Sanctuaries? State its features and objectives.
Answer: Sanctuaries are the places where the animals are well protected from any disturbance.
Objectives:
- Conservation of species and inhabitants by manipulative management.
- Protect ecosystem i.e. flora, fauna, wildlife, natural landscape
- Educate people and create awareness about ecological balance.
Features
- No human resides in the sanctuary, other than a public servant on duty and permitted persons by the Chief Wildlife Warden.
- Restricted human activities.
Zone
- Contains core, buffer and restoration zone.
There are 551 existing wildlife sanctuaries in India.
Q20: What are biosphere reserve? State its features and objectives.
Answer: Biosphere reserves are the large areas meant to protect biodiversity. These are Multi-purpose protected areas.
Objectives:
- Conservation of the natural resources and for the improvement of the relationship between man and the environment therein.
- Educate people and create awareness.
- Conservation of landscapes, ecosystems, species and genetic variation
Features
- Both natural and human-influenced ecosystems;
- human settlements allowed (rural) in the outermost zone.
Zone
- Core, Buffer, restoration and cultural
There are total 11 biosphere reserves of India which have been recognized internationally under Man and Biosphere Reserve program.
The programme of Biosphere Reserve was initiated under the 'Man & Biosphere’ (MAB) programme by UNESCO in 1971. These reserves are internationally recognised.
Q21: What are the main objectives and advantages of biodiversity conservation?
Answer: Main objectives and advantages of biodiversity conservation are:
① To preserve the continuity of the food chain.
② To preserve and protect the genetic diversity of plants and animals.
③ To provide benefits to the society such as recreation and tourism and maintain ecological balance.
④ To ensure the sustainable utilization of life support systems on earth
Q22: Define species.
Answer: Species is a group of population which is capable of interbreeding,
Q23: What are endemic species? Give two examples of endemic species in India.
Answer: Endemic species are those species of plant or animals which are found exclusively in a particular area.
They are not found anywhere else. A Particular type of animal or plant may be endemic to zone, state or country.
.Examples of Endemic Species In India:
1. Nilgiri Wood-Pigeon
2. Indian Bustard
3. Asiatic Lion, Gir Forest
4. Lion-Tailed Macaque, Western Ghats
5. Nilgai
6. Waxflower
7. Indian Giant Squirrel.
Q24: What are endangered species?
Answer: Species with low population numbers that are in considerable danger of becoming extinct is termed as Endangered Species.
For example, tiger, rhinos, saltwater crocodile, dolphins of river Ganges, gharials are included in the list of endangered species.
To protect these endangered species, there are many projects which were launched by the Government of India. Such as:
- Project Tiger,
- Project Elephant,
- Operation Rhino,
- Gir Lion Project
- Crocodile Breeding Project
Q25: Write a short note on the project tiger.
Answer:
1. The population of Tiger (Panthera tigris) reduced from about 40,000 to 1827 in 1972.
2. In 1, April 1973, Project Tiger was launched by Government of India, which resulted in an increase in the population of the tiger.
3. Various tiger reserves were created in the country based on the 'core-buffer' strategy, e.g. Sundarbans Tiger reserve, Sariska Conservation Unit etc.
4. Their natural habitats are restored, tigers are protected from poaching.
5. In 2018, the number of tigers in India is around 2,967.
Q26: What is a red data book?
Answer: Red Data Book is a record book that contains a record of animals which are identified as endangered species or animals which are on the verge of extinction. The book is maintained by International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN).
Q27: Name the following:
(a) National Animal
(b) National Bird
(c) National Flower
(d) National Fruit
(e) National Tree
(f) National Heritage Animal
Answer:
(a) Tiger
(b) Peacock
(c) Lotus
(d) Mango
(e) Banyan Tree
(f) Elephant animal
Q28: Why do bird migrate?
Answer: A groups of animals (especially birds or fishes) periodically move from one region to another for feeding and breeding. Such movements are generally seasonal journeys. Birds migrate and cover large distances in response to changes in food availability, habitat or weather.
The regular, periodic, two-way movements of birds and some animals from their place of residence to some other place along well-defined routes. Bird migration is linked to seasonal factors, breeding, shortage of foods, etc. The Bharatpur bird sanctuary is known for the migratory birds.
Q29: What are extinct species? Give examples.
Answer: Species of plants and animals which have already been lost. Example: Dodo, Indian cheetah, Pink-headed duck, etc.
Q30: Define reforestation. How is it different from afforestation?
Answer: Reforestation is the restocking of destroyed forests by planting new trees. Afforestation refers to planting trees on patches of land which were not previously covered in forest.
Q31: What is Van Mahotsav? What is its importance?
Answer: Van Mahotsav is an annual tree-planting movement in India which initially began in 1950. The name Van Mahotsav means the festival of trees. It is celebrated in the first week of July. It has gained significant importance every year. Millions of saplings are planted across India in observation of Van Mahotsav by government agencies and NGOs. The importance of the festival is to grow more trees, save forests and bring awareness among people about ill-effects of deforestation and to understand people about ecological balance.
☞See also:
Ch 7 - Conservation of Plants and Animals(Q & A)
Ch7 - Conservation of Plants and Animals(MCQs)
Ch 7 - Importance of Forest Resources



No comments:
Post a Comment
We love to hear your thoughts about this post!
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.