CBSE Class 9 - Circles - NCERT Exercise 10.2 + Questions
Question 1: Recall that two circles are congruent if they have the same radii. Prove that equal chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres.
Answer:
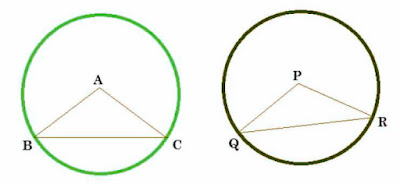
Given: Circle C (A, r) and C (P, r) are two congruent circles such that BC = QR.
To prove: ∠BAC = ∠QPR
Proof: In ∆ABC and ∆PQR,
BC = QR [ Given]
AB = PQ [ Radii of congruent circles]
AC = PR [ Radii of congruent circles]
Hence, ∆ABC ≅ ∆PQR [SSS Congruency rule]
∴ ∠BAC = ∠QPR [CPCT]
Question 2: Prove that if chords of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres, then the chords are equal.
Answer:
Given: Two congruent circles with centres O and O'. AB and CD are chords of circles with centre O and O' respectively such that ∠AOB = ∠CO'D
To Prove: AB = CD
Proof: In triangles AOB and CO'D,
AO = CO'
BO = DO' [Radii of congruent circle]
∠AOB = ∠CO'D [Given]
∆AOB ≅ ∆CO'D [SAS axiom]
AB = CD Proved. [CPCT]
Question 3 (MCQ): Number of circles that can be drawn passing through two points are
(a) one
(b) two
(c) infinite
(d) no circle can be drawn
Answer: (c) infinite
Question 4 (MCQ): The collection of all points in a plane which are at a fixed distance from a given point of the plane is called
(a) Centre
(b) Circumference
(c) Radius
(d) Circle
Answer: (d) Circle
Question 5 (Fill in the blanks): The fixed point is called the _______ of the circle and the fixed distance is called the of the circle.
Answer: centre, radius
Question 6(MCQ): The longest chord of a circle is called
(a) Radius
(b) Segment
(c) Diameter
(d) Circumference
Answer: (c) Diameter
👉See Also:
Ch 10 Circles (Important Terms To Remember)
Ch 10 Circles (Worksheet)
Ch 10 Circles (NCERT Ex 10.1)
Ch 10 Circles (Quiz)


No comments:
Post a Comment
We love to hear your thoughts about this post!
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.