Crop Production and Management
 |
| Types of Crops (based on Seasons) |
Questions and Answers based on Class 8 NCERT Chapter
Q1: Define agriculture.
Answer: It is a science that deals with the growth of plants and animals for human use is called agriculture.
Answer: When plants of the same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is known as a crop. For example, crop of wheat means that all the plants grown in a field are that of wheat.
Answer: All the activities which are involved in the cultivation of crops from sowing to harvesting are known as agricultural practices.
Answer: Following are the reasons that India need improved agricultural practices:
i. India's population is around 1.20 Billion and it is growing faster than its ability to produce wheat and rice.
ii. To provide sufficient food to such a large population, it is required to maintain regular production and proper crop management.
iii. It requires an improvement in agricultural practices and application of latest technology.
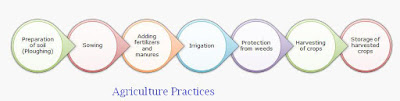
Q5: List the seven agricultural practices.
Answer:
i. Preparation of soil
ii. Sowing
iii. Adding manure and fertilisers
iv. Irrigation
v. Protecting from weeds
vi. Harvesting
vii. Storage
Q6: Name the cropping patterns which based on season are found in India?
Answer:
i. Kharif Crops
ii. Rabi Crops
iii. Zaid Crops
Q7: In which season Kharif crops are sown?
Answer: Rainy Season (July to September)
Q8: Give two examples of Kharif crops.
Answer: Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton,
Q9: In which season Rabi crops are sown?
Answer: Rabi crops are grown in the winter season (October to March).
Q10: Give examples of Rabi crops.
Answer: Wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed.
Q11: Give examples of Zaid Crops.
Answer: Watermelon, Muskmelon, , bitter gourd, pumpkin, cucumber etc.
Q12: List the methods involved in preparing a soil.
Answer:
i. Ploughing or Tilling
ii. Levelling
iii. Tilling
Q13: Why does the soil need to be turned and loosened?
Q: What is the importance of Ploughing?
Answer:
i. Loosening brings the nutrients rich soil to the top and in this way the plants can easily absorb the nutrients available in the soil.
ii. It retains moisture for a long period.
iii. It provides good aeration to roots in order to breathe.
iv. It removes the unwanted plants (weeds).
Q14: Name the different types of implements used in ploughing.
Answer: Plough, Hoe, Cultivator.
Q15: What is the use of Plank?
Answer: The ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs. Plank is used to break these crumbs.
Q16: List the three parts of Plough.
Answer: Ploughshare, Ploughshaft and Beam.
Q17: How cultivator is better than a traditional wooden plough?
Answer: A cultivator is a modern tool which is attached to the back of a tractor. This type of ploughing reduces the need of more man-power and time for ploughing the fields.
Q18: What is levelling? How does it help?
Answer: The ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs. It is necessary to break these crumbs with the leveller (e.g. plank). It ensures uniform irrigation.
Q19: Why does manure is sometimes added during tilling?
Answer: Because this helps in proper mixing of manure with soil.
Q20: What is sowing?
Answer: Planting of seeds in the soil is known as sowing. This is done after ploughing the field.
Q21: What types of seeds are chosen in sowing?
Answer: Seeds should be good quality, high yielding, healthy and free from infection.
Q22: Name the two methods of sowing.
Answer: Broadcasting and seed drill.
Q23: A farmer took some seeds of wheat from a bag and dropped those seeds in a beaker half-filled with water. He found seeds floating on the water. He took seeds from the second bag and repeated the test. Seeds from the second bag sank into the beaker. Which seeds he should choose for sowing?
Answer: Seeds from second bag which are healthy. Seeds in bag A are damaged. These damaged seeds become hollow and are thus lighter. Therefore, they float on water.
Q24: What is broadcasting?
Answer: It is the traditional method of sowing where the seeds are sown manually by scattering them in the moist soil.
Q25: Why is seed drilling method better than broadcasting?
Answer: Seed drilling is better method because:
i. It helps in uniform distribution of seeds.
ii. It covers the seed after sowing. This prevents the seeds from being damaged by birds.
iii. It saves time and labour.
Q26: What is nursery? Give examples of two plants grown in a nursery.
Answer: A nursery is a place where plants are grown to an appropriate size (plantlets) and then these are transplanted to fields. Paddy (Rice), flowering plants are first grown in nursery.
Q27: Why is overcrowding of plants avoided?
Answer: To avoid overcrowding of plants, seeds are sown at appropriate distances. This allows plants to get sufficient sunlight, nutrients and water
from the soil.
Q28: Why are manures and fertilizers required?
Answer: Continuous growing of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients. The crops consume the nutrients from the soil and make it infertile. Manures and fertilizers replenish the soil with the nutrients.
Q29: Apart from manuring what are other methods to replenish the nutrients of the soil?
Answer: Field fallowing and Crop rotation.
Q30: Why is organic manure considered better alternative to fertilizers?
Answer: Organic manure is made to replenish the soil with all the nutrients.
- It not only increases the water holding capacity of the soil but also improves the quality of soil.
- Unlike fertilizers they do not pollute water.
- It increases the number of friendly microbes.
- It improves the texture of the soil.
Q31: Give three examples of fertilisers.
Answer: Urea, ammonium sulphate, super phosphate, potash, NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium).
Q32: Define irrigation.
Answer: The process of supplying water to crops in the field at different intervals is called irrigation.
Q33: Name the sources of irrigation.
Answer: The sources of irrigation are— wells, tubewells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.
Q34: List the traditional ways of irrigation? Are these ways better than modern methods?
Answer: Traditional methods of irrigation are:
i. Moat (pulley system)
ii. chain pump
iii. dhekli
iv. rahat (lever system)
Traditional methods are cheaper but not efficient once compared to modern methods.
Q35: What are the modern methods of irrigation?
Answer:
a) Sprinkler Irrigation
b) Drip System
c) Furrow Irrigation
d) Basin Irrigation
Q36: Where is sprinkler system more useful?
Answer: Sprinkler irrigation method is useful where the soil cannot retain water for a long time e.g. sandy soil. It is useful on uneven land where sufficient water is not available like lawn.
Q37: What is drip irrigation?
Answer: In this irrigation water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots, it is called drip irrigation. It is the best method to
save water. It is widely used to irrigate fruit plants and gardens e.g. grapes, banana, brinjal, etc.,
Q38: What are weeds? Give two examples.
Answer: Weeds are undesirable plants growing naturally along with the crop. Grass are Amaranthus examples of weeds.
Q39: Why is weeding necessary?
Answer: Weeds need to be removed because:
i. They compete with crops for water, nutrients, space and light. It affects the growth of crops.
ii. Some weeds are poisonous to animals and humans.
Q40: What are different methods of weeding?
Answer:
i. Manual Weeding: Plucking with the help of tools like khurpa, harrow etc.
ii. Chemical Methods: Use of weedicides like Dalapon, metachlor etc
iii. Bio-Weedicides: Use of certain type of fungi and bacteria.
Q41: Define harvesting.
Answer: The process of cutting and gathering a matured crop, either manually or by machines, is known as harvesting.
Q42: List the Indian festivals associated with harvesting.
Answer:
- Baisakhi, Holi (Northern India e.g. Punjab, Uttar Pradesh)
- Pongal (Tamilnadu)
- Bihu (Assam)
- Onam (Kerala)
Q45: What is threshing?
Answer: The process of separating grains from stalk is called threshing.
Q46: What are silos?
Answer: Very tall cemented tanks used to store grains at large scale are called silos.
Q46: What type of storage is used to store fruits and vegetables?
Answer: Fresh fruits and vegetables have moisture content. They get spoilt soon. Thet are stored in cold storage.
Q47: How do standards of cereals, pulses are maintained in India?
Answer: AGMARK is the certification mark given on agricultural products (crops, pulses, vegetable oils etc.). Various AGMARK laboratories setup through out India, perform tests and give grading to the agricultural products.
Q48: What is animal husbandry?
Answer: Rearing of animals for commercial purposes is called animal husbandry.
Answer: It is a science that deals with the growth of plants and animals for human use is called agriculture.
Q2: Define Crop
Answer: When plants of the same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is known as a crop. For example, crop of wheat means that all the plants grown in a field are that of wheat.
Q3: What are agricultural practices?
Answer: All the activities which are involved in the cultivation of crops from sowing to harvesting are known as agricultural practices.
Q4: Why does India need improved agricultural practices?
Answer: Following are the reasons that India need improved agricultural practices:
i. India's population is around 1.20 Billion and it is growing faster than its ability to produce wheat and rice.
ii. To provide sufficient food to such a large population, it is required to maintain regular production and proper crop management.
iii. It requires an improvement in agricultural practices and application of latest technology.
Q5: List the seven agricultural practices.
Answer:
i. Preparation of soil
ii. Sowing
iii. Adding manure and fertilisers
iv. Irrigation
v. Protecting from weeds
vi. Harvesting
vii. Storage
Q6: Name the cropping patterns which based on season are found in India?
Answer:
i. Kharif Crops
ii. Rabi Crops
iii. Zaid Crops
Q7: In which season Kharif crops are sown?
Answer: Rainy Season (July to September)
Q8: Give two examples of Kharif crops.
Answer: Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton,
Q9: In which season Rabi crops are sown?
Answer: Rabi crops are grown in the winter season (October to March).
Q10: Give examples of Rabi crops.
Answer: Wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed.
Q11: Give examples of Zaid Crops.
Answer: Watermelon, Muskmelon, , bitter gourd, pumpkin, cucumber etc.
Q12: List the methods involved in preparing a soil.
Answer:
i. Ploughing or Tilling
ii. Levelling
iii. Tilling
Q13: Why does the soil need to be turned and loosened?
or
Answer:
i. Loosening brings the nutrients rich soil to the top and in this way the plants can easily absorb the nutrients available in the soil.
ii. It retains moisture for a long period.
iii. It provides good aeration to roots in order to breathe.
iv. It removes the unwanted plants (weeds).
Q14: Name the different types of implements used in ploughing.
Answer: Plough, Hoe, Cultivator.
Q15: What is the use of Plank?
Answer: The ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs. Plank is used to break these crumbs.
Q16: List the three parts of Plough.
Answer: Ploughshare, Ploughshaft and Beam.
Q17: How cultivator is better than a traditional wooden plough?
Answer: A cultivator is a modern tool which is attached to the back of a tractor. This type of ploughing reduces the need of more man-power and time for ploughing the fields.
Q18: What is levelling? How does it help?
Answer: The ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs. It is necessary to break these crumbs with the leveller (e.g. plank). It ensures uniform irrigation.
Q19: Why does manure is sometimes added during tilling?
Answer: Because this helps in proper mixing of manure with soil.
Q20: What is sowing?
Answer: Planting of seeds in the soil is known as sowing. This is done after ploughing the field.
Q21: What types of seeds are chosen in sowing?
Answer: Seeds should be good quality, high yielding, healthy and free from infection.
Q22: Name the two methods of sowing.
Answer: Broadcasting and seed drill.
Q23: A farmer took some seeds of wheat from a bag and dropped those seeds in a beaker half-filled with water. He found seeds floating on the water. He took seeds from the second bag and repeated the test. Seeds from the second bag sank into the beaker. Which seeds he should choose for sowing?
Answer: Seeds from second bag which are healthy. Seeds in bag A are damaged. These damaged seeds become hollow and are thus lighter. Therefore, they float on water.
Q24: What is broadcasting?
Answer: It is the traditional method of sowing where the seeds are sown manually by scattering them in the moist soil.
Q25: Why is seed drilling method better than broadcasting?
Answer: Seed drilling is better method because:
i. It helps in uniform distribution of seeds.
ii. It covers the seed after sowing. This prevents the seeds from being damaged by birds.
iii. It saves time and labour.
Q26: What is nursery? Give examples of two plants grown in a nursery.
Answer: A nursery is a place where plants are grown to an appropriate size (plantlets) and then these are transplanted to fields. Paddy (Rice), flowering plants are first grown in nursery.
Q27: Why is overcrowding of plants avoided?
Answer: To avoid overcrowding of plants, seeds are sown at appropriate distances. This allows plants to get sufficient sunlight, nutrients and water
from the soil.
Q28: Why are manures and fertilizers required?
Answer: Continuous growing of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients. The crops consume the nutrients from the soil and make it infertile. Manures and fertilizers replenish the soil with the nutrients.
Q29: Apart from manuring what are other methods to replenish the nutrients of the soil?
Answer: Field fallowing and Crop rotation.
Q30: Why is organic manure considered better alternative to fertilizers?
Answer: Organic manure is made to replenish the soil with all the nutrients.
- It not only increases the water holding capacity of the soil but also improves the quality of soil.
- Unlike fertilizers they do not pollute water.
- It increases the number of friendly microbes.
- It improves the texture of the soil.
Q31: Give three examples of fertilisers.
Answer: Urea, ammonium sulphate, super phosphate, potash, NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium).
Q32: Define irrigation.
Answer: The process of supplying water to crops in the field at different intervals is called irrigation.
Q33: Name the sources of irrigation.
Answer: The sources of irrigation are— wells, tubewells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.
Q34: List the traditional ways of irrigation? Are these ways better than modern methods?
Answer: Traditional methods of irrigation are:
i. Moat (pulley system)
ii. chain pump
iii. dhekli
iv. rahat (lever system)
Traditional methods are cheaper but not efficient once compared to modern methods.
Q35: What are the modern methods of irrigation?
Answer:
a) Sprinkler Irrigation
b) Drip System
c) Furrow Irrigation
d) Basin Irrigation
Q36: Where is sprinkler system more useful?
Answer: Sprinkler irrigation method is useful where the soil cannot retain water for a long time e.g. sandy soil. It is useful on uneven land where sufficient water is not available like lawn.
Q37: What is drip irrigation?
Answer: In this irrigation water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots, it is called drip irrigation. It is the best method to
save water. It is widely used to irrigate fruit plants and gardens e.g. grapes, banana, brinjal, etc.,
Q38: What are weeds? Give two examples.
Answer: Weeds are undesirable plants growing naturally along with the crop. Grass are Amaranthus examples of weeds.
Q39: Why is weeding necessary?
Answer: Weeds need to be removed because:
i. They compete with crops for water, nutrients, space and light. It affects the growth of crops.
ii. Some weeds are poisonous to animals and humans.
Q40: What are different methods of weeding?
Answer:
i. Manual Weeding: Plucking with the help of tools like khurpa, harrow etc.
ii. Chemical Methods: Use of weedicides like Dalapon, metachlor etc
iii. Bio-Weedicides: Use of certain type of fungi and bacteria.
Q41: Define harvesting.
Answer: The process of cutting and gathering a matured crop, either manually or by machines, is known as harvesting.
Q42: List the Indian festivals associated with harvesting.
Answer:
- Baisakhi, Holi (Northern India e.g. Punjab, Uttar Pradesh)
- Pongal (Tamilnadu)
- Bihu (Assam)
- Onam (Kerala)
Q45: What is threshing?
Answer: The process of separating grains from stalk is called threshing.
Q46: What are silos?
Answer: Very tall cemented tanks used to store grains at large scale are called silos.
Q46: What type of storage is used to store fruits and vegetables?
Answer: Fresh fruits and vegetables have moisture content. They get spoilt soon. Thet are stored in cold storage.
Q47: How do standards of cereals, pulses are maintained in India?
Answer: AGMARK is the certification mark given on agricultural products (crops, pulses, vegetable oils etc.). Various AGMARK laboratories setup through out India, perform tests and give grading to the agricultural products.
Q48: What is animal husbandry?
Answer: Rearing of animals for commercial purposes is called animal husbandry.

Very good and appropriate answers ,easy to understand by a student .
ReplyDelete