Class 12 - Biology - Understanding Immunity (Q & A) - Chapter: Human Health and Diseases
Q1: Define immunity.
Answer: Immunity means resistance to infections and antigens. Immunity is the capacity of an organism to resist or defend itself from the development of a disease.
Q2: What is an antigen? Give some examples.
Answer: Any substance or molecule that induces the immune system to produce antibodies against it is called an antigen. Examples include pathogens, virus, pollens, chemicals etc.
Q3: Name two main types of immunities.
Answer:
1. Innate immunity
2. Acquired immunity
Q4: What is innate immunity?
Answer: Innate immunity is inherited by the organism from the parents and present at the time of birth.
Q5: Explain the four types barriers of innate immunity.
Answer: Innate immunity consists of four types of barriers :
(a) Physical Barriers: prevent entry of microorganisms in the body e.g. skin, mucus coating of epithelium of respiratory, gastrointestinal and urinogenital tracts.
(b) Physiological Barriers: prevent microbial growth in the body. e.g. acid of stomach, lysozymes of saliva and tears
(c) Cellular Barriers: are phagocytes and destroy microbes e.g. PMNL, monocytes, neutrophils and macrophases
(d) Cytokine barriers : are virus infected cells secrete proteins called interferons which protect non-infected cells from further infection.
Q6: What is an acquired immunity? List its important features.
Answer: Acquired immunity is not present since birth. It is developed during individual's lifetime.
(i) It is pathogen specific and is characterised by memory,
(ii) When it encounters a pathogen for the first time, it produces a response called primary response, which is of low intensity,
(iii) Further encounter with same pathogen produces highly intensified secondary or anamnestic response due to memory of the first encounter.
(iv) Immune responses are produced by lymphocytes (B-cells and T-cells)
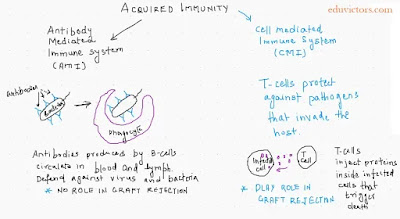
Q7: Based on defense mechanism, how acquired immunity is classified?
Answer: Two types of acquired immunity:
(a) Humoral immune response or Antibody Mediated Immunity (AMI)
It is mediated by antibodies present in blood and lymph.
(b) Cell-mediated immune response or Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI)
It is mediated by T-lymphocytes. The graft rejection during organ transplantation, because of the ability to differentiate between self and non-self, is due to the cell-mediated immunity.
Q8: What are antibodies?
Answer: Antibodies are immunoglobulin protein molecules (Ig). These are protective proteins produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign substance. There are of five types of antibodies: IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE
Q9: Draw the structure of an antibody molecule.
Answer: Each antibody molecule has four peptide chains, i.e. two small called light (L) chains and two longer called heavy (H) chains. Hence, an antibody is represented as H^.
Q10: Tabulate four differences between active immunity and passive immunity.
Answer:
| Active Immunity | Passive Immunity |
|---|---|
| 1. Body prepares antibody itself due to exposure of antigen (Pathogen). Example : Typhoid vaccination | 1. Preformed antibodies are injected in the body in case of deadly microbe attack. Example : Anti-snake venom, ATS. |
| 2. Immunity is not immediate | 2. Very quick immune response. |
| 3. It has very few side effects. | 3. May show side effects like allergic reaction. |
| 4. It lasts for long period. | 4. It lasts for limited period. |
Kingdom Fungi (AIPMT MCQs)
Plant Nutrition MCQs (AIPMT/NEET)
Plants Of Special Interests (Pre-Medical)
Environmental Biology MCQs (AIPMT/NEET)
Genetics MCQs (AIPMPT/NEET)
Evolution (Very Short Question Answers)
Famous Indian Biologists
Animal Nutrition and Digestive System (AIPMT MCQs)
Human Nutrition (Worksheet)
Five Digestive Juices
List of Important Proteins
Human Reproduction (Important Terms)
Human Reproduction System (Very Short Q & A)
HIV/AIDS (A Brief Introduction)
AIPMT/NEET Biology Quiz-1
An overview of Virus and Viroids (Q & A)



No comments:
Post a Comment
We love to hear your thoughts about this post!
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.