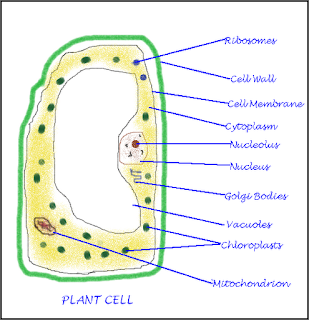
Coal and Petroleum
(NCERT Exemplar Q & A)
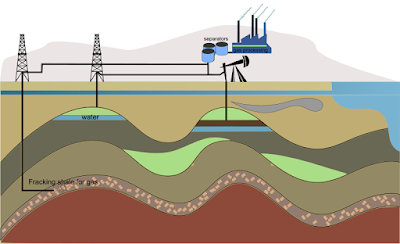 |
| Petroleum Refinery |
Question 1: You are provided with a mixture of petroleum and water. Can you suggest a method to separate the two?
Answer: Decantation
Question 2: What does CNG stand for and why is it considered to be a better fuel then petrol?
Answer: CNG stands for compressed natural gas. It is considered to be a better fuel because it is less polluting.
Question 3: Name the petroleum product used as fuel for stoves, lamps and jet aircrafts.
Answer: Kerosene is used as fuel for stove,lamps and jet aircrafts.
Question 4: Fill in the blanks in the following sentences.
1. Coal is one of the ________ used to cook food.
2. When heated in air, coal burns and produces mainly _________ gas.
3. Coal Tar is a black, thick - with an ________ smell.
4. Petroleum, ______ and _______ are fossil fuels.
5. Forest and coal are _________ natural resources.