Blog provides NCERT solutions, CBSE, NTSE, Olympiad study material, model test papers, important Questions and Answers asked in CBSE examinations. References to Educational Sites and resources.
Wednesday, 23 December 2015
CBSE Class 9 - Geography - CH6 - Population (Q and A)
Population
Q & A based on NCERT Chapter
Q1: What are the three components of the study of population?
Answer:
i. Population size and distribution
ii. Population growth and purposes of population change.
iii. Characteristics or qualities of the population
Q2: Define Population census.
Answer: It is the total process of collecting, compiling, analysing, or otherwise disseminating demographic economic and social data pertaining at a specific time of all persons in a country.
Q3: Which state has the lowest population?
Answer: Sikkim
Q4: What is meant by density of population?
Answer: The number of persons per sq. km is called density of population.
Q5: Which is the most populous state of India?
Answer: Uttar Pradesh

Monday, 21 December 2015
CBSE Class 7 - Science - CH 8 - Wastewater Story (MCQs)
Wastewater Story
 |
| Waster Water Treatment Workflow Leonard G. at English Wikipedia [CC BY-SA 2.5 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5)], via Wikimedia Commons |
MCQs based on NCERT Chapter
Q1: The light materials which float during waste water treatment is
(a) sludge
(b) scum
(c) sewerage
(d) biogas
Q2: Which of the following is produced during waste water treatment?
(a) sludge
(b) biogas
(c) both biogas and sludge
(d) none of these
Q3: Contaminated water disease is
(a) gastroenteritis
(b) malaria
(c) flu
(d) none of these
Q4: Which of the following is a part of waste water treatment plant?
(a) clarifier
(b) aeration tank
(c) vertical bars
(d) all of these

Sunday, 20 December 2015
CBSE Class 10 - Economics - Chapter 3 - Money and Credit (Short Q and A)
Money and Credit
Short Question and Answers based on NCERT Chapter
Q1: Define money?
Answer: It is defined as medium of exchange.
Q2: What does money serve?
Answer: Money serves as :
a. a unit of accounting
b. a store of value or purchasing power
c. a standard of deferred payment
Q3: What is Double Coincidence of Wants?
Answer: It refers to a situation wherein what a person wishes to sell is exactly the same as that the other person wishes to buy.
Q4: In which situation Double Coincidence of Wants is the most suitable?
Answer: In barter system.
Q5: What is the form of money in Ancient Period?
Answer: Grain and cattle (Barter System)

Saturday, 19 December 2015
Friday, 18 December 2015
Thursday, 17 December 2015
CBSE Class 6 - Our Pasts - CH 8 - Ashoka, The Emperor Who Gave Up War (Q and A)
Ashoka, The Emperor
Who Gave Up War
Q& A based on NCERT Chapter 8
 |
| Ashoka Pillar - National Emblem Can you tell how many lions are there in the emblem? image credits: AS Mysore For Vincent Arthur Smith |
Q.1 Name the ruler who spread Buddhism all over the world.
Answer: Ashoka
Q.2 Who wrote Arthshastra? What is it about?
Answer: Chanakya wrote Arthshastra. Many of Chanakya's ideas about how to rule a kingdom were written in it.
Q.3 Name two languages used during Ashokan period.
Answer: Prakrit and Sanskrit were used during Ashokan period.
Q.4 Who was Seleucus Nicator?
Answer: Seleucus Nicator was the greek ruler of West Asia.
Q.5 What do you mean by Dynasty?
Answer: When members of the same family become rulers one after another, the family is often called dynasty.

Wednesday, 16 December 2015
CBSE Class 9/10 - English - Reading Comprehension Passage (Set-7)
Reading Comprehension Passage
From CBSE Class 10 Sample Question Paper
When my maternal uncle was alive, his only son quietly made plans to settle in Germany with his wife. Without informing his father or sister he bought tickets ‘and sold all movable things at home. A week before he left, everyone was informed of his plans. People criticised him for abandoning his father. The married daughter who was settled in Bhopal, shifted to Delhi to look after her father. A year later the father was admitted to a private hospital and died. The son came from Germany, paid the bills and performed all the death ceremonies.
People now said that after all, he had come all the way so he was not a bad son. No word about how he had neglected his father or how his sister had to disrupt her personal life to take care of old Dad.
This is what life teaches every daughter. That our society values a son more because he has the religious sanction to perform death ceremonies and grant them liberation - (Mukti). A daughter may have given them love, care, sensitivity, time, service, but the son gets preference because he carries forward the family name and performs shraadh. He may be uncaring, arrogant and indifferent but for parents, a son is their treasure.
Two years back in our neighbourhood a man died without leaving a will. His only son sold the bungalow and took away his sick mother without informing his three sisters who then approached the courts for a share of the property. Is this the family structure we boast of to the world? Where do love and laughter vanish when siblings become adults? Are we right in blaming a newlywed for poisoning a son’s brain? Love for a daughter has to come from within. Saints repeatedly clarify that death ceremonies need not be performed only by one’s own son. And what guarantee is there that a son will perform the shraadh? If parents do not reciprocate a daughter’s love, won’t Heaven, which claims to be just and fair, reproaches them for their insensitivity?
Questions

Tuesday, 15 December 2015
CBSE Class 9/10/11/12 - Cloze Test -2 (English Grammar)
Cloze Test
The League of Nations was (1) in 1919. It became ineffective and the UNO began to (2) from October 24, 1945. The Second World War (3) in 1939. It caused great (4) to human lives and properly. As a (5) of use of atom bombs, many people were (6) and many became (7). The world leaders feared that another world war would (8) the entire world. It was a question of the (9) of mankind. To ensure peace and (10) the world leaders established world organisation, the UNO.
1. (A) created
(B) formed
(C) made
(D) opened
2. (A) start
(B) operate
(C) function
(D) commence
3. (A) broke in
(B) broke out
(C) broke into
(D) broke up
4. (A) wastage
(B) calamity
(C) loss
(D) disturbance

Sunday, 13 December 2015
CBSE Class 9 - Science - Work, Energy and Power - Numerical Problems
Work, Energy and Power
Numerical Problems based on Class 9 Physics NCERT Chapter
Q1(CBSE 2012): State the relation between the commercial unit of energy and joules.
Answer: Kilowatt hour (kWh)
1 kwh - 3.6 x 106 joules
Q2: How much work is done on a body of mass 1kg whirling on a circular path of radius 5m?
Answer: Zero
Q3: A body of mass 15 kg undergoes downward displacement of 40m under the effect of gravitational force. How much work is done? (take g = 10 m/s2)
Answer:
Given
acceleration (a) = g = 10 m/s2
mass (m) = 15 kg
displacement (s) = 40 m
Work W = F × s
= m × a × s = 15 × 10 × 40 = 6000 J
Since gravitational force and displacement are in the same direction, work is said to be positive and done on the body.
Q4: A body of mass 120 g is taken vertically upwards to reach the height of 5m. Calculate work done. (Take g = 10 m/s2)
Answer: Given,
a = g = - 10 m/s2
m = 120g = 0.120 kg
s = 5m
Work W = F × s
= m × g × s = 0.12 × -10 × 5 = -6 J
a = g = - 10 m/s2
m = 120g = 0.120 kg
s = 5m
Work W = F × s
= m × g × s = 0.12 × -10 × 5 = -6 J
Since Force and displacement act in opposite directions, work is negative. Here work is considered to be done by the body against the applied force.
Q5: A momentum of the body is increased by 20%. What is the percentage increase in its kinetic energy?

Saturday, 12 December 2015
CBSE Class 9/10 - Hindi (B) - संधि-विच्छेद
संधि-विच्छेद
दिए गए विकल्पों में से उचित संधि-विच्छेद छांटकर लिखो-
१. प्रत्येक
क. प्रत्य + एक
ख. प्रति + अक
ग. प्रत + एक
घ. प्रति + एक
२. यथेष्ट
क. यथा + इष्ट
ख. यथे + इष्ट
ग. यथे + ष्ट
घ. यथ + इष्ट
३. स्वागत
क. स्व + आगत
ख. स्वा + गत
ग. सु + आगत
घ. सु + वागत
४. सर्वोत्तम
क. सर्वो + उत्तम
ख. सर्व + उत्तम
ग. सर्वो + त्तम
घ. सर्वोत्त + म
५. गुरूपदेश
क. गुरु + उपदेश
ख. गुरू + उपदेश
ग. गुरू + पदेश
घ. गुरूप + देश

Friday, 11 December 2015
CBSE Class 6 - Science - CH 8 - Body Movements (Worksheet)
Body Movements
Worksheet based on NCERT Chapter
 |
| Types of Joints in Human Skeleton credits: By OpenStax College [CC BY 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons |
Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
1. The bony framework which gives shape to the body is called ___________.
2. The skeletal system is comprised of __________, ___________ and _____________.
3. Small bones that make up the back bone are known as _____________.
4. Give an example of pivot joint.
____________________________________________________.
5. Movement is brought about by the contraction and relaxation of ____________.

Wednesday, 9 December 2015
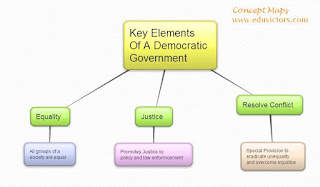
CBSE Class 6 - Social And Political Life- Chapter 4 - Key Elements Of A Democratic Government (Short Q and A)
Key Elements Of A Democratic Government
Short Q & A based on NCERT Chapter
Q.1 What is apartheid?
Answer: Apartheid means separation or discrimination on the basis of race. South African people were divided into white, black, Indian and coloured races.
Q.2 Which languages were spoken in South Africa?
Answer: Zulu and Afrikaans were spoken in South Africa.
Q.3 What is the full form of ANC?
Answer: African National Congress. This party led the struggle against Apartheid or racism.
Q.4 Name a famous leader of ANC.
Answer: Nelson Mandela
Q.5 How often elections are held in India?
Answer: Elections are held after every five years.
CBSE Class 9 Maths - SA2 - Sample Question Paper (2012)
CBSE Class IX - Maths- SA2- Sample Question Paper (2012)
The sample paper is based on old pattern, still it is good for practice.

Monday, 7 December 2015
CBSE Class 12 - Business Studies - Marketing vs Selling
Marketing Management
Marketing vs Selling
 |
| credits: Wasi at Wikimedia |
Q: Distinguish between Marketing and Selling on the basis of
(a) Meaning
(b) Objective
(c) Scope
(d) Importance
(e) Orientation
(f) Point of Start
(g) Approach
(h) Control
(i) Price
(j) Technology Focus
Answer:

Sunday, 6 December 2015
CBSE Class 8 - Our Pasts - Ch3 - Ruling The Country Side (NCERT Solution)
Ruling The Country Side
 |
| Nil Darpan - A famous Bengali play written by Dinbandhu Mitra. The play talks about NilBidroha or The Blue Rebellion or Indigo Revolt |
NCERT Chapter Q & A
Q1: Match the following:
(a) ryot (i) village
(b) mahal (ii) peasant
(c) nij (iii) cultivation on ryot’s lands
(d) ryoti (iv) cultivation on planter’s own land
Answer:
(a) ryot - peasant
(b) mahal - village
(c) nij - cultivation on planter’s own land
(d) ryoti - cultivation on planter’s own land
Q2: Fill in the blanks:
(a) Growers of woad in Europe saw __________ as a crop which would provide competition to their earnings.
(b) The demand for indigo increased in lateeighteenth-century Britain because of __________.
(c) The international demand for indigo was affected by the discovery of __________.
(d) The Champaran movement was against __________.
Answer: (a) indigo
(b) industrialisation which expanded cotton production and created demand for cloth dyes.
(c) synthetic dyes
(d) indigo planters
Q3: Describe the main features of the Permanent Settlement.
Answer:
- Permanent Settlement was introduced by Eas India Company in 1793.
- By the terms of the settlement, the rajas and taluqdars were recognised as zamindars.
- Zamindars would collect rent from the peasants and pay revenue to the Company.
- It would ensure a regular flow of revenue into the Company’s coffers and encourage the zamindars to invest in improving the land.
- But this settlement created problems. Zamindars found revenue rates were too high and they found it difficult to pay.

Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)

