CBSE Class 8 - General Science - Unit Test Paper - 1 (2017-18)
Chapters covered:1. Microorganisms
2. Metals and Non-Metals
3. Force and Pressure
Blog provides NCERT solutions, CBSE, NTSE, Olympiad study material, model test papers, important Questions and Answers asked in CBSE examinations. References to Educational Sites and resources.

 |
| Let's move the rock! |


 |
| Resin Coding System (Image Credits: Openclipart) |





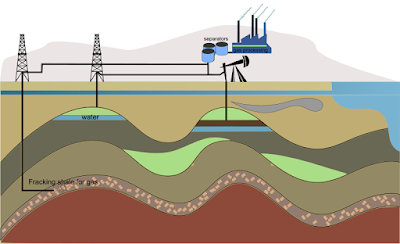 |
| Petroleum Refinery |


| Property | Metals | Non Metals |
|---|---|---|
| Physical State | Most metals are solids at room temperature except mercury which is a liquid. Gallium and Cesium also changes into liquid at slightly above room temperature. | Non Metals exist in all states. Eleven are gases, bromine is liquid while others are solids. |
| Melting and Boiling Point | Generally have high melting and boiling points. (Exceptions are Gallium, Mercury, Sodium and Potassium.) | Generally they have low melting and boiling points. Exceptions are: Carbon, Boron and Silicon. |
| Density | They have high density except Sodium and potassium. | Low denisty (Diamond is an exception.) |
| Lusture | Metals shine and are lustrous. | Non-metalls appear dull. (Exceptions are Diamond, graphite and iodine.) |


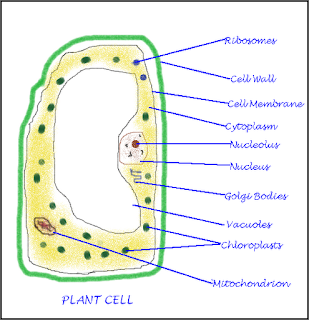
| Organelles | Present In | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Plants only | Outer most covering, stiff shape, made of cellulose | Protects the cell from temperature variation, inside water pressure and moisture, procvides structural strength |
| Cell Membrane | Both plants and animals | Plants inside the cell wall. Animal: thin outermost selectively permeable |
Allows exchange of selected substance, supports the cell, separates the cell from its environment. |
| Nucleus | Both plants and animals | Oval shaped body | Control cell activities, transmits genetics characteristics |
| Cytoplasm | Both plants and animals | Thick jelly like fluid containing other cell organelles | Site of all life (metabolic) processes, protects cell organelles |
| Mitochondria | Both plants and animals | Rod shaped body | Site of respiration, releases energy form sugar, called power house of the cell |
| Golgi body | Both plants and animals | Parallel stacked vesicles | packaging and dispatch of proteins and lipids, helps in lysosomes formation |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Both plants and animals | Networks of tubes and membrane | Transportation of materials. |
| Ribosomes | Both plants and animals | Small bodies, sometimes attached to endoplasmic reticulum | protein synthesis |
| Vacuole | Plant: single and large. Animal: very small or absent |
Sac-like structure in cytoplasm | Stores food and water (cell sap) |
| Plastids | Only Plants | Small colored bodies in cytoplasm | Impart color to leaf, flower and fruit |
| Lysosomes | Generally animals | Membrane bound sac in cytoplasm filled with digestive enzymes | Eats up(digests) damaged cells and unwanted cell products |

| Metal | Main Uses |
|---|---|
| Iron | Bridges, Train tracks, Construction Bars, Steel, Engine Parts, Iron sheets etc. |
| Copper | Electrical Wires, Utensils, Coins etc. |
| Aluminium | Electric Wires, Utensils, Airplanes, Metallic Paints, Foil for packaging etc. |
| Silver | Jewellery, Electroplating, photography, Utensils, Coins, silvering of mirrors etc. |
| Gold | Jewellery and Decorations, Coins |
| Lead | Batteries, Alloys, Paints, Alloys like solder, Protective screen for X-Rays etc. |
| Mercury | Thermometers, Barometers, Dental amalgams etc. |

 |
| Forest Fires - Why do forests catch fire in hot summers? |

 |
| Fungal Infected Bread |

Please turn off the ad blocker. This is only way that we can earn some penny. Please support us by trun off the ad blocker.
Thank you!!